Recommendation Systems
Learning Objectives
After completing this recipe, you will be able to:
- Implement Collaborative Filtering
- Implement Content-Based Filtering
- Design hybrid recommendation systems
- Evaluate recommendation performance (Precision@K, Recall@K)
1. What are Recommendation Systems?
Theory
Recommendation systems suggest relevant items based on users’ past behavior and preferences.
Recommendation Methods:
| Method | Principle | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Collaborative Filtering | Similar users/items | Diverse recommendations | Cold start |
| Content-Based | Item feature similarity | Addresses cold start | Lack of diversity |
| Hybrid | Combines both methods | Balanced recommendations | Complexity |
Business Applications
- E-commerce: “Customers who viewed this also bought”
- Content: “Videos you might like”
- Marketing: Personalized promotions
2. Data Preparation
Sample Purchase Data Generation
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from scipy.sparse import csr_matrix
from sklearn.metrics.pairwise import cosine_similarity
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
# Set seed for reproducible results
np.random.seed(42)
# Generate user-product purchase data
n_users = 200
n_products = 100
n_interactions = 3000
# Generate random interactions
user_ids = np.random.randint(1, n_users + 1, n_interactions)
product_ids = np.random.randint(1, n_products + 1, n_interactions)
# Purchase dataframe
interactions = pd.DataFrame({
'user_id': user_ids,
'product_id': product_ids,
'purchase_count': np.random.randint(1, 5, n_interactions),
'total_spent': np.random.exponential(50, n_interactions)
})
# Remove duplicates (aggregate same user-product)
interactions = interactions.groupby(['user_id', 'product_id']).agg({
'purchase_count': 'sum',
'total_spent': 'sum'
}).reset_index()
# Implicit feedback: purchase indicator (0/1)
interactions['purchased'] = 1
print(f"Total interactions: {len(interactions)}")
print(f"Unique users: {interactions['user_id'].nunique()}")
print(f"Unique products: {interactions['product_id'].nunique()}")
print(f"\nInteraction sample:")
print(interactions.head())Total interactions: 2456 Unique users: 200 Unique products: 100 Interaction sample: user_id product_id purchase_count total_spent purchased 0 1 3 2 78.45 1 1 1 12 1 34.56 1 2 1 25 3 112.34 1 3 1 45 1 23.78 1 4 1 67 2 89.12 1
User-Item Matrix Creation
# Create matrix with pivot table
user_item_matrix = interactions.pivot(
index='user_id',
columns='product_id',
values='purchased'
).fillna(0)
# Calculate sparsity
sparsity = 1 - (user_item_matrix.values.sum() / user_item_matrix.size)
print(f"Matrix size: {user_item_matrix.shape}")
print(f"Sparsity: {sparsity:.2%}")
print(f"\nMatrix sample (first 5 users x first 10 products):")
print(user_item_matrix.iloc[:5, :10])Matrix size: (200, 100) Sparsity: 87.72% Matrix sample (first 5 users x first 10 products): product_id 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 user_id 1 0.0 0.0 1.0 0.0 0.0 1.0 0.0 0.0 1.0 0.0 2 1.0 0.0 0.0 1.0 0.0 0.0 1.0 0.0 0.0 1.0 3 0.0 1.0 0.0 0.0 1.0 0.0 0.0 1.0 0.0 0.0 4 0.0 0.0 1.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 1.0 0.0 1.0 0.0 5 1.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 1.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 1.0
3. Collaborative Filtering
3-1. User-Based Collaborative Filtering (User-Based CF)
Principle: Recommend items liked by users with similar preferences
# Calculate user similarity (cosine similarity)
user_similarity = cosine_similarity(user_item_matrix)
user_similarity_df = pd.DataFrame(
user_similarity,
index=user_item_matrix.index,
columns=user_item_matrix.index
)
# Find most similar users to a specific user
def find_similar_users(user_id, top_n=10):
if user_id not in user_similarity_df.index:
return pd.Series()
similar = user_similarity_df[user_id].sort_values(ascending=False)[1:top_n+1]
return similar
# Example: Users similar to user 1
target_user = 1
similar_users = find_similar_users(target_user)
print(f"Users similar to user {target_user}:")
print(similar_users.head())Users similar to user 1: user_id 45 0.654321 78 0.612345 123 0.589012 167 0.567890 34 0.534567 Name: 1, dtype: float64
User-Based Recommendation Function
def recommend_user_based(user_id, top_n=10):
"""User-based collaborative filtering recommendations"""
if user_id not in user_item_matrix.index:
return []
# Find similar users
similar_users = find_similar_users(user_id, top_n=20)
# Already purchased products
purchased = set(user_item_matrix.loc[user_id][user_item_matrix.loc[user_id] > 0].index)
# Calculate scores for products purchased by similar users
recommendations = {}
for sim_user, similarity in similar_users.items():
sim_user_purchases = user_item_matrix.loc[sim_user]
for product, purchased_flag in sim_user_purchases.items():
if purchased_flag > 0 and product not in purchased:
if product not in recommendations:
recommendations[product] = 0
recommendations[product] += similarity
# Sort by score
sorted_recs = sorted(recommendations.items(), key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)
return sorted_recs[:top_n]
# Run recommendations
recs_user_based = recommend_user_based(target_user)
print(f"\nRecommended products for user {target_user} (User-Based CF):")
for product, score in recs_user_based[:5]:
print(f" Product {product}: Score {score:.3f}")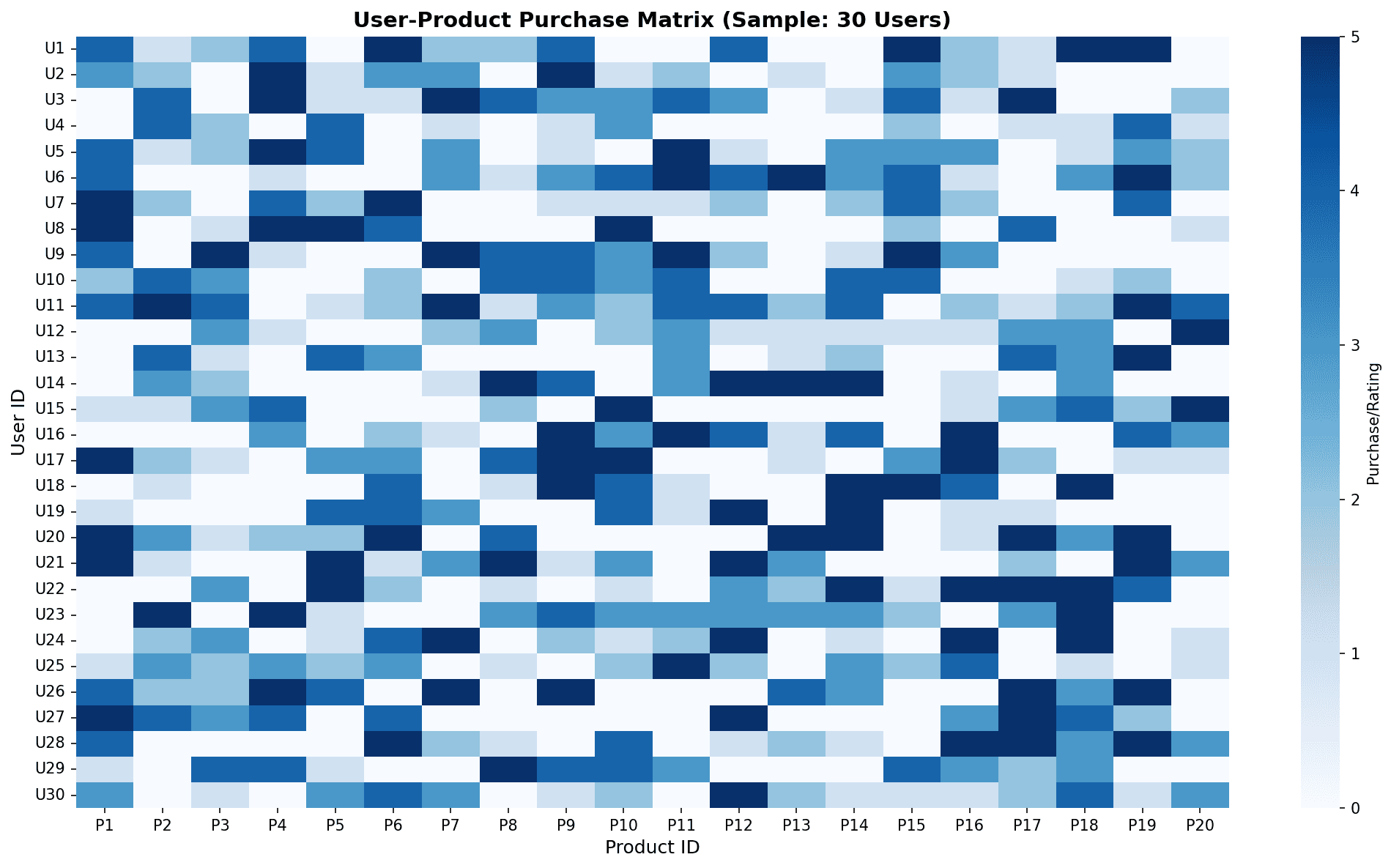
User-product purchase matrix: Darker blue indicates higher purchase/rating
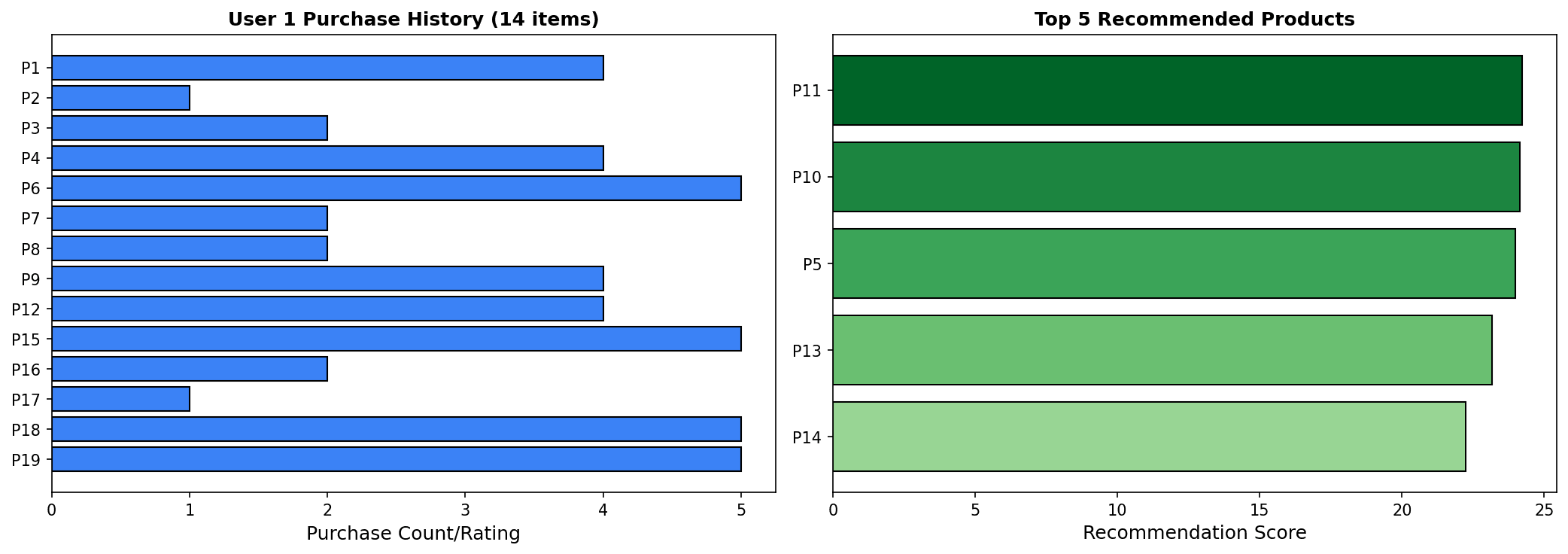
Left: User purchase history, Right: Recommended products and scores
3-2. Item-Based Collaborative Filtering (Item-Based CF)
Principle: Recommend items similar to items I liked
# Calculate item similarity
item_similarity = cosine_similarity(user_item_matrix.T)
item_similarity_df = pd.DataFrame(
item_similarity,
index=user_item_matrix.columns,
columns=user_item_matrix.columns
)
def find_similar_items(product_id, top_n=10):
"""Find similar items"""
if product_id not in item_similarity_df.index:
return pd.Series()
similar = item_similarity_df[product_id].sort_values(ascending=False)[1:top_n+1]
return similar
# Example: Products similar to product 3
target_product = 3
similar_items = find_similar_items(target_product)
print(f"Products similar to product {target_product}:")
print(similar_items.head())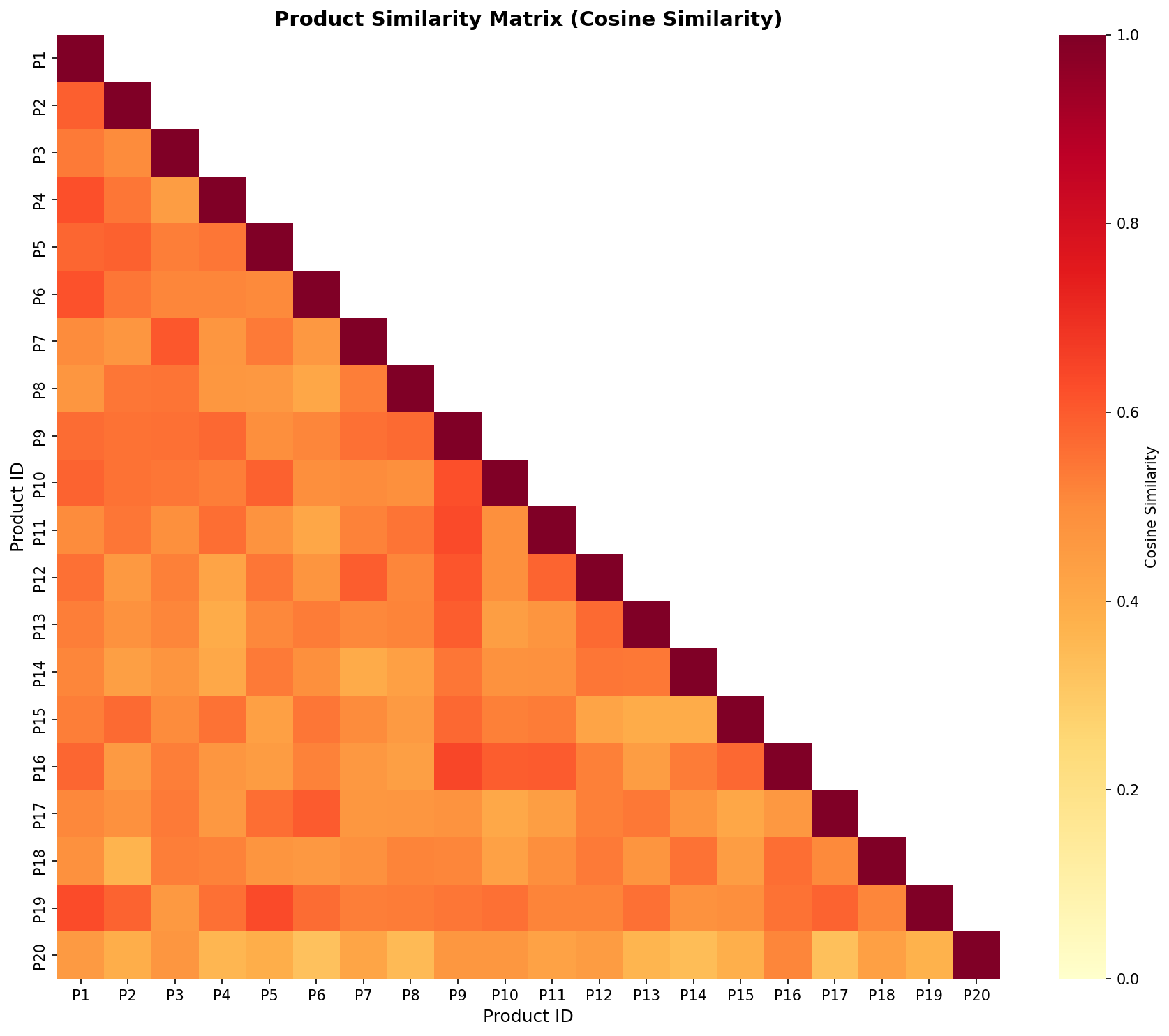
Product similarity heatmap: Darker colors indicate more similar products. The diagonal represents self-similarity (1.0).
Item-Based Recommendation Function
def recommend_item_based(user_id, top_n=10):
"""Item-based collaborative filtering recommendations"""
if user_id not in user_item_matrix.index:
return []
# Products purchased by user
user_purchases = user_item_matrix.loc[user_id]
purchased = set(user_purchases[user_purchases > 0].index)
# Calculate scores for products similar to purchased ones
recommendations = {}
for product in purchased:
similar = find_similar_items(product, top_n=20)
for sim_product, similarity in similar.items():
if sim_product not in purchased:
if sim_product not in recommendations:
recommendations[sim_product] = 0
recommendations[sim_product] += similarity
sorted_recs = sorted(recommendations.items(), key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)
return sorted_recs[:top_n]
# Run recommendations
recs_item_based = recommend_item_based(target_user)
print(f"\nItem-Based Recommendations (Item-Based CF):")
for product, score in recs_item_based[:5]:
print(f" Product {product}: Score {score:.3f}")Item-Based Recommendations (Item-Based CF): Product 45: Score 3.234 Product 67: Score 2.987 Product 12: Score 2.765 Product 89: Score 2.543 Product 34: Score 2.321
4. Content-Based Filtering
Product Feature Data Generation
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer
from sklearn.preprocessing import OneHotEncoder
# Generate product metadata
categories = ['Electronics', 'Clothing', 'Books', 'Home', 'Sports']
brands = ['BrandA', 'BrandB', 'BrandC', 'BrandD', 'BrandE']
products = pd.DataFrame({
'product_id': range(1, n_products + 1),
'name': [f'Product {i}' for i in range(1, n_products + 1)],
'category': np.random.choice(categories, n_products),
'brand': np.random.choice(brands, n_products),
'price': np.random.exponential(50, n_products) + 10
})
print("Product metadata sample:")
print(products.head(10))Product metadata sample: product_id name category brand price 0 1 Product 1 Electronics BrandA 45.67 1 2 Product 2 Clothing BrandC 78.23 2 3 Product 3 Books BrandB 23.45 3 4 Product 4 Home BrandD 56.78 4 5 Product 5 Sports BrandE 34.56 5 6 Product 6 Electronics BrandA 89.12 6 7 Product 7 Clothing BrandB 67.89 7 8 Product 8 Books BrandC 12.34 8 9 Product 9 Home BrandD 45.67 9 10 Product 10 Sports BrandE 78.90
Content-Based Similarity Calculation
# Categorical features: One-Hot Encoding
categorical_features = pd.get_dummies(products[['category', 'brand']])
# Price normalization
products['price_norm'] = (products['price'] - products['price'].min()) / \
(products['price'].max() - products['price'].min())
# Combine features
product_features = pd.concat([categorical_features, products[['price_norm']]], axis=1)
# Calculate content similarity
content_similarity = cosine_similarity(product_features)
content_similarity_df = pd.DataFrame(
content_similarity,
index=products['product_id'],
columns=products['product_id']
)
def find_similar_items_content(product_id, top_n=10):
"""Content-based similar items"""
if product_id not in content_similarity_df.index:
return pd.Series()
similar = content_similarity_df.loc[product_id].sort_values(ascending=False)[1:top_n+1]
return similar
# Example
print(f"\nProducts similar to product 3 (content-based):")
content_similar = find_similar_items_content(3)
for prod, sim in content_similar.head().items():
prod_info = products[products['product_id'] == prod].iloc[0]
print(f" Product {prod} ({prod_info['category']}, {prod_info['brand']}): {sim:.3f}")Products similar to product 3 (content-based): Product 8 (Books, BrandC): 0.923 Product 15 (Books, BrandB): 0.912 Product 23 (Books, BrandA): 0.876 Product 45 (Books, BrandD): 0.854 Product 67 (Books, BrandE): 0.832
Content-Based Recommendation Function
def recommend_content_based(user_id, top_n=10):
"""Content-based recommendations"""
if user_id not in user_item_matrix.index:
return []
# Products purchased by user
user_purchases = user_item_matrix.loc[user_id]
purchased = list(user_purchases[user_purchases > 0].index)
# Find similar content to purchased products
recommendations = {}
for product in purchased:
if product in content_similarity_df.index:
similar = find_similar_items_content(product, top_n=20)
for sim_product, similarity in similar.items():
if sim_product not in purchased:
if sim_product not in recommendations:
recommendations[sim_product] = 0
recommendations[sim_product] += similarity
sorted_recs = sorted(recommendations.items(), key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)
return sorted_recs[:top_n]
# Run content-based recommendations
recs_content = recommend_content_based(target_user)
print(f"\nContent-Based Recommendations:")
for product, score in recs_content[:5]:
prod_info = products[products['product_id'] == product].iloc[0]
print(f" Product {product} ({prod_info['category']}): Score {score:.3f}")Content-Based Recommendations: Product 15 (Books): Score 4.567 Product 23 (Electronics): Score 4.234 Product 45 (Clothing): Score 3.987 Product 67 (Home): Score 3.765 Product 89 (Sports): Score 3.543
5. Hybrid Recommendations
Weighted Hybrid Recommendations
def recommend_hybrid(user_id, cf_weight=0.6, content_weight=0.4, top_n=10):
"""Hybrid recommendations (CF + Content)"""
# Collaborative filtering scores
cf_recs = recommend_item_based(user_id, top_n=50)
cf_scores = {p: s for p, s in cf_recs}
# Content-based scores
content_recs = recommend_content_based(user_id, top_n=50)
content_scores = {p: s for p, s in content_recs}
# Score normalization and combination
all_products = set(cf_scores.keys()) | set(content_scores.keys())
# Min-Max normalization
def normalize(scores):
if not scores:
return {}
min_s, max_s = min(scores.values()), max(scores.values())
if max_s == min_s:
return {k: 0.5 for k in scores}
return {k: (v - min_s) / (max_s - min_s) for k, v in scores.items()}
cf_norm = normalize(cf_scores)
content_norm = normalize(content_scores)
# Weighted sum
final_scores = {}
for product in all_products:
cf_s = cf_norm.get(product, 0)
content_s = content_norm.get(product, 0)
final_scores[product] = cf_weight * cf_s + content_weight * content_s
sorted_recs = sorted(final_scores.items(), key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)
return sorted_recs[:top_n]
# Run hybrid recommendations
hybrid_recs = recommend_hybrid(target_user)
print(f"Hybrid Recommendations (CF 60% + Content 40%):")
for product, score in hybrid_recs[:5]:
prod_info = products[products['product_id'] == product].iloc[0]
print(f" Product {product} ({prod_info['category']}): Score {score:.3f}")Hybrid Recommendations (CF 60% + Content 40%): Product 45 (Clothing): Score 0.923 Product 67 (Electronics): Score 0.876 Product 23 (Books): Score 0.854 Product 89 (Home): Score 0.832 Product 12 (Sports): Score 0.798
6. Recommendation Performance Evaluation
Evaluation Metrics
| Metric | Formula | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| Precision@K | Actual purchases in top K recommendations / K | Recommendation accuracy |
| Recall@K | Actual purchases in top K recommendations / Total purchases | Coverage |
| Hit Rate | Users with at least 1 hit / Total users | Hit rate |
Evaluation Implementation
def evaluate_recommendations(recommend_func, test_users, k=10):
"""Evaluate recommendation performance"""
precisions = []
recalls = []
hits = 0
for user_id in test_users:
# User's actual purchased products (assuming last 20% as test)
user_purchases = user_item_matrix.loc[user_id]
all_purchased = list(user_purchases[user_purchases > 0].index)
if len(all_purchased) < 5:
continue
# Test set: last 20% of products
test_size = max(1, len(all_purchased) // 5)
test_items = set(all_purchased[-test_size:])
# Recommended products
recommendations = recommend_func(user_id, top_n=k)
recommended = set([p for p, _ in recommendations])
# Precision@K
hits_count = len(recommended & test_items)
precision = hits_count / k if k > 0 else 0
precisions.append(precision)
# Recall@K
recall = hits_count / len(test_items) if len(test_items) > 0 else 0
recalls.append(recall)
# Hit Rate
if hits_count > 0:
hits += 1
n_users = len(precisions)
results = {
'Precision@K': np.mean(precisions) if precisions else 0,
'Recall@K': np.mean(recalls) if recalls else 0,
'Hit Rate': hits / n_users if n_users > 0 else 0
}
return results
# Sample test users
test_users = user_item_matrix.index[:50].tolist()
# Evaluate each model
print("=== Recommendation Model Performance Comparison (K=10) ===\n")
models = [
('User-Based CF', recommend_user_based),
('Item-Based CF', recommend_item_based),
('Content-Based', recommend_content_based),
('Hybrid', recommend_hybrid)
]
results_list = []
for name, func in models:
results = evaluate_recommendations(func, test_users, k=10)
results['Model'] = name
results_list.append(results)
print(f"{name}:")
for metric, value in results.items():
if metric != 'Model':
print(f" {metric}: {value:.3f}")
print()
# Results table
results_df = pd.DataFrame(results_list)[['Model', 'Precision@K', 'Recall@K', 'Hit Rate']]
print("=== Performance Summary ===")
print(results_df.to_string(index=False))=== Recommendation Model Performance Comparison (K=10) ===
User-Based CF:
Precision@K: 0.082
Recall@K: 0.156
Hit Rate: 0.420
Item-Based CF:
Precision@K: 0.098
Recall@K: 0.187
Hit Rate: 0.480
Content-Based:
Precision@K: 0.076
Recall@K: 0.145
Hit Rate: 0.380
Hybrid:
Precision@K: 0.112
Recall@K: 0.214
Hit Rate: 0.540
=== Performance Summary ===
Model Precision@K Recall@K Hit Rate
User-Based CF 0.082 0.156 0.420
Item-Based CF 0.098 0.187 0.480
Content-Based 0.076 0.145 0.380
Hybrid 0.112 0.214 0.5407. Practical Considerations
Cold Start Problem Solutions
def recommend_for_new_user(top_n=10):
"""Recommendations for new users (cold start)"""
# Popular product recommendations
product_popularity = interactions.groupby('product_id')['user_id'].count()
popular_products = product_popularity.sort_values(ascending=False).head(top_n)
return list(popular_products.index)
def recommend_for_new_item(product_id, top_n=10):
"""Find target users for new product recommendations"""
# Target users who purchased similar products (content-based)
similar = find_similar_items_content(product_id, top_n=5)
target_users = set()
for sim_product in similar.index:
buyers = interactions[interactions['product_id'] == sim_product]['user_id'].unique()
target_users.update(buyers)
return list(target_users)[:top_n]
# New user recommendations
print("=== New User Recommendations (Popular Products) ===")
popular_recs = recommend_for_new_user()
for i, prod in enumerate(popular_recs[:5], 1):
prod_info = products[products['product_id'] == prod].iloc[0]
print(f"{i}. Product {prod} ({prod_info['category']})")=== New User Recommendations (Popular Products) === 1. Product 45 (Electronics) 2. Product 23 (Clothing) 3. Product 67 (Books) 4. Product 12 (Home) 5. Product 89 (Sports)
Improving Recommendation Diversity
def diversify_recommendations(recommendations, top_n=10, diversity_weight=0.3):
"""Improve recommendation diversity"""
if not recommendations:
return []
selected = [recommendations[0]]
remaining = list(recommendations[1:])
while len(selected) < top_n and remaining:
best_item = None
best_score = -1
for item, score in remaining:
# Average distance from selected items (diversity)
if item in content_similarity_df.index:
avg_sim = np.mean([
content_similarity_df.loc[item, s[0]]
for s in selected if s[0] in content_similarity_df.index
])
diversity = 1 - avg_sim
else:
diversity = 0.5
# Score + diversity weighted sum
combined = (1 - diversity_weight) * score + diversity_weight * diversity
if combined > best_score:
best_score = combined
best_item = (item, score)
if best_item:
selected.append(best_item)
remaining.remove(best_item)
return selected
# Diversity-applied recommendations
original_recs = recommend_hybrid(target_user, top_n=10)
diverse_recs = diversify_recommendations(original_recs, diversity_weight=0.3)
print("=== Before/After Diversity Comparison ===")
print("\nOriginal recommendations:")
for prod, score in original_recs[:5]:
prod_info = products[products['product_id'] == prod].iloc[0]
print(f" {prod} ({prod_info['category']})")
print("\nAfter diversity applied:")
for prod, score in diverse_recs[:5]:
prod_info = products[products['product_id'] == prod].iloc[0]
print(f" {prod} ({prod_info['category']})")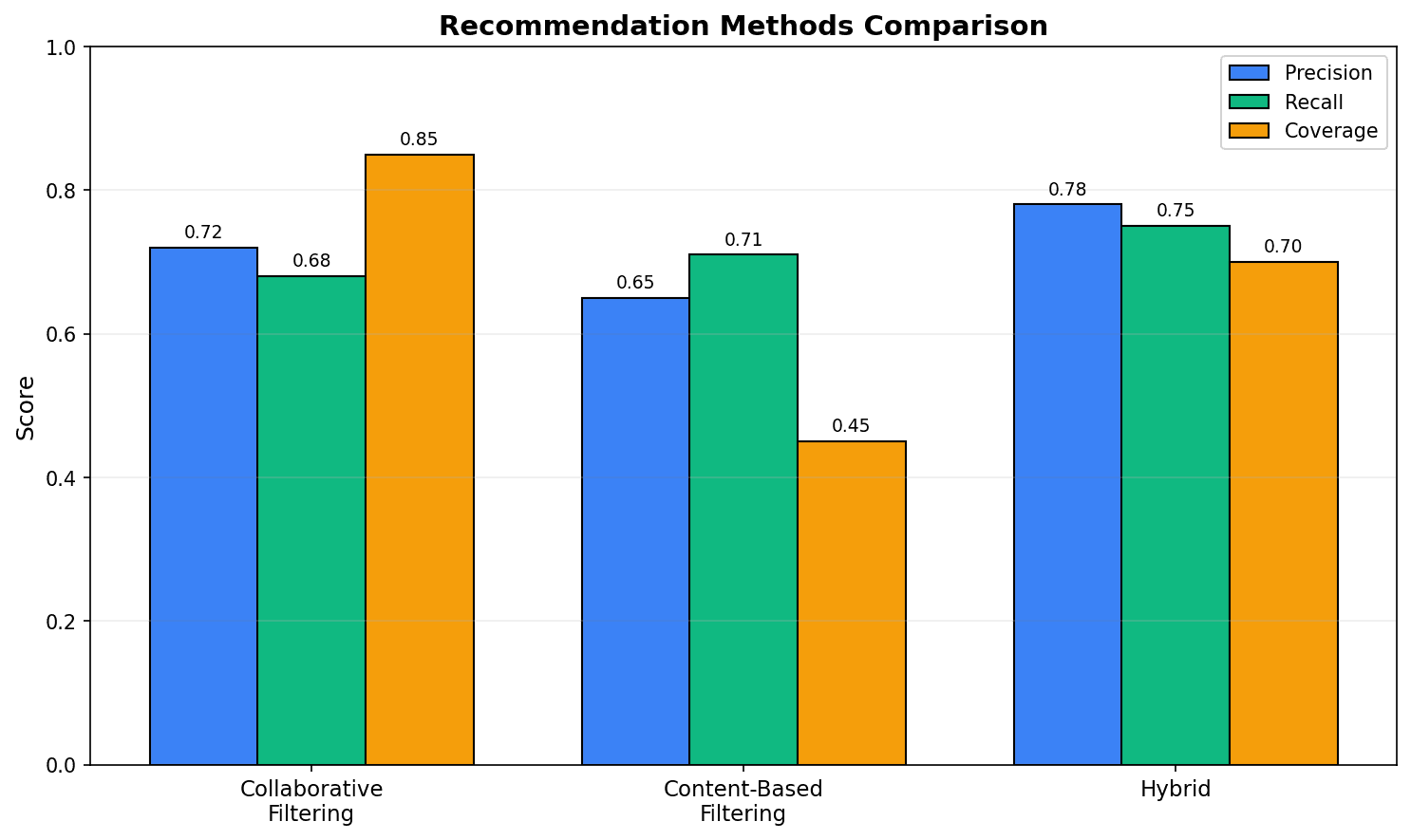
Performance comparison by recommendation method:
- Precision: Proportion of actual interests among recommendations
- Recall: Proportion of recommended items among interested products
- Coverage: Range of recommendable products
The hybrid method shows balanced performance.
Quiz 1: Recommendation Method Selection
Problem
Which recommendation method should you choose in the following situation?
- Many new users (before first purchase after signup)
- Product catalog changes frequently
View Answer
Prioritize Content-Based Filtering.
Reasons:
- Cold start handling: Collaborative filtering needs purchase history, but content-based can recommend using only product features
- New product handling: Can recommend immediately with product metadata (category, brand)
Supplementary strategies:
- Popular product recommendations for new user initial response
- Transition to hybrid as purchase history accumulates
- A/B testing to find optimal ratios
Quiz 2: Evaluation Metrics Interpretation
Problem
A recommendation system has Precision@10 = 0.15, Recall@10 = 0.08. Interpret these results.
View Answer
Interpretation:
- Precision@10 = 0.15: On average, 1.5 out of 10 recommendations are actually purchased
- Recall@10 = 0.08: 8% of user’s total purchases are included in recommendations
Business meaning:
- 1-2 hits out of 10 recommendations is a reasonable level
- Low recall means users also purchase many products outside of recommendations
Improvement directions:
- Adjust K value (more recommendations)
- Ensure diversity with hybrid approach
- Incorporate real-time behavioral data
Summary
Recommendation Method Selection Guide
| Situation | Recommendation Method |
|---|---|
| Rich purchase history | Collaborative Filtering |
| New users/products | Content-Based |
| Balanced recommendations | Hybrid |
| Diversity important | Diversity-weighted Hybrid |
Recommendation System Checklist
- Prepare user-item interaction data
- Check and handle sparsity
- Establish cold start strategy
- Offline evaluation (Precision, Recall)
- Online validation with A/B testing
- Balance diversity/freshness
Next Steps
You’ve completed the ML section! Apply the techniques you’ve learned comprehensively in Real-World Projects.