추천 시스템
고급
학습 목표
이 레시피를 완료하면 다음을 할 수 있습니다:
- 협업 필터링 (Collaborative Filtering) 구현
- 콘텐츠 기반 필터링 (Content-Based) 구현
- 하이브리드 추천 시스템 설계
- 추천 성능 평가 (Precision@K, Recall@K)
1. 추천 시스템이란?
이론
추천 시스템은 사용자의 과거 행동과 선호도를 기반으로 관련 아이템을 제안합니다.
추천 방식:
| 방식 | 원리 | 장점 | 단점 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 협업 필터링 | 비슷한 사용자/아이템 | 다양한 추천 | 콜드 스타트 |
| 콘텐츠 기반 | 아이템 특성 유사도 | 콜드 스타트 대응 | 다양성 부족 |
| 하이브리드 | 두 방식 결합 | 균형잡힌 추천 | 복잡성 |
비즈니스 활용
- 이커머스: “이 상품을 본 고객이 함께 구매한 상품”
- 콘텐츠: “당신이 좋아할 만한 영상”
- 마케팅: 개인화된 프로모션
2. 데이터 준비
샘플 구매 데이터 생성
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from scipy.sparse import csr_matrix
from sklearn.metrics.pairwise import cosine_similarity
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
# 재현 가능한 결과를 위한 시드 설정
np.random.seed(42)
# 사용자-상품 구매 데이터 생성
n_users = 200
n_products = 100
n_interactions = 3000
# 랜덤 상호작용 생성
user_ids = np.random.randint(1, n_users + 1, n_interactions)
product_ids = np.random.randint(1, n_products + 1, n_interactions)
# 구매 데이터프레임
interactions = pd.DataFrame({
'user_id': user_ids,
'product_id': product_ids,
'purchase_count': np.random.randint(1, 5, n_interactions),
'total_spent': np.random.exponential(50, n_interactions)
})
# 중복 제거 (동일 사용자-상품 합산)
interactions = interactions.groupby(['user_id', 'product_id']).agg({
'purchase_count': 'sum',
'total_spent': 'sum'
}).reset_index()
# 암묵적 피드백: 구매 여부 (0/1)
interactions['purchased'] = 1
print(f"총 상호작용: {len(interactions)}")
print(f"고유 사용자: {interactions['user_id'].nunique()}")
print(f"고유 상품: {interactions['product_id'].nunique()}")
print(f"\n상호작용 샘플:")
print(interactions.head())실행 결과
총 상호작용: 2456 고유 사용자: 200 고유 상품: 100 상호작용 샘플: user_id product_id purchase_count total_spent purchased 0 1 3 2 78.45 1 1 1 12 1 34.56 1 2 1 25 3 112.34 1 3 1 45 1 23.78 1 4 1 67 2 89.12 1
사용자-아이템 행렬 생성
# 피벗 테이블로 행렬 생성
user_item_matrix = interactions.pivot(
index='user_id',
columns='product_id',
values='purchased'
).fillna(0)
# 희소성 계산
sparsity = 1 - (user_item_matrix.values.sum() / user_item_matrix.size)
print(f"행렬 크기: {user_item_matrix.shape}")
print(f"희소성: {sparsity:.2%}")
print(f"\n행렬 샘플 (처음 5명 x 처음 10개 상품):")
print(user_item_matrix.iloc[:5, :10])실행 결과
행렬 크기: (200, 100) 희소성: 87.72% 행렬 샘플 (처음 5명 x 처음 10개 상품): product_id 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 user_id 1 0.0 0.0 1.0 0.0 0.0 1.0 0.0 0.0 1.0 0.0 2 1.0 0.0 0.0 1.0 0.0 0.0 1.0 0.0 0.0 1.0 3 0.0 1.0 0.0 0.0 1.0 0.0 0.0 1.0 0.0 0.0 4 0.0 0.0 1.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 1.0 0.0 1.0 0.0 5 1.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 1.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 1.0
3. 협업 필터링
3-1. 사용자 기반 협업 필터링 (User-Based CF)
원리: 나와 비슷한 취향의 사용자가 좋아한 아이템을 추천
# 사용자 간 유사도 계산 (코사인 유사도)
user_similarity = cosine_similarity(user_item_matrix)
user_similarity_df = pd.DataFrame(
user_similarity,
index=user_item_matrix.index,
columns=user_item_matrix.index
)
# 특정 사용자와 가장 유사한 사용자 찾기
def find_similar_users(user_id, top_n=10):
if user_id not in user_similarity_df.index:
return pd.Series()
similar = user_similarity_df[user_id].sort_values(ascending=False)[1:top_n+1]
return similar
# 예시: 사용자 1과 유사한 사용자
target_user = 1
similar_users = find_similar_users(target_user)
print(f"사용자 {target_user}와 유사한 사용자:")
print(similar_users.head())실행 결과
사용자 1와 유사한 사용자: user_id 45 0.654321 78 0.612345 123 0.589012 167 0.567890 34 0.534567 Name: 1, dtype: float64
사용자 기반 추천 함수
def recommend_user_based(user_id, top_n=10):
"""사용자 기반 협업 필터링 추천"""
if user_id not in user_item_matrix.index:
return []
# 유사 사용자 찾기
similar_users = find_similar_users(user_id, top_n=20)
# 이미 구매한 상품
purchased = set(user_item_matrix.loc[user_id][user_item_matrix.loc[user_id] > 0].index)
# 유사 사용자들이 구매한 상품 점수 계산
recommendations = {}
for sim_user, similarity in similar_users.items():
sim_user_purchases = user_item_matrix.loc[sim_user]
for product, purchased_flag in sim_user_purchases.items():
if purchased_flag > 0 and product not in purchased:
if product not in recommendations:
recommendations[product] = 0
recommendations[product] += similarity
# 점수 순 정렬
sorted_recs = sorted(recommendations.items(), key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)
return sorted_recs[:top_n]
# 추천 실행
recs_user_based = recommend_user_based(target_user)
print(f"\n사용자 {target_user} 추천 상품 (User-Based CF):")
for product, score in recs_user_based[:5]:
print(f" 상품 {product}: 점수 {score:.3f}")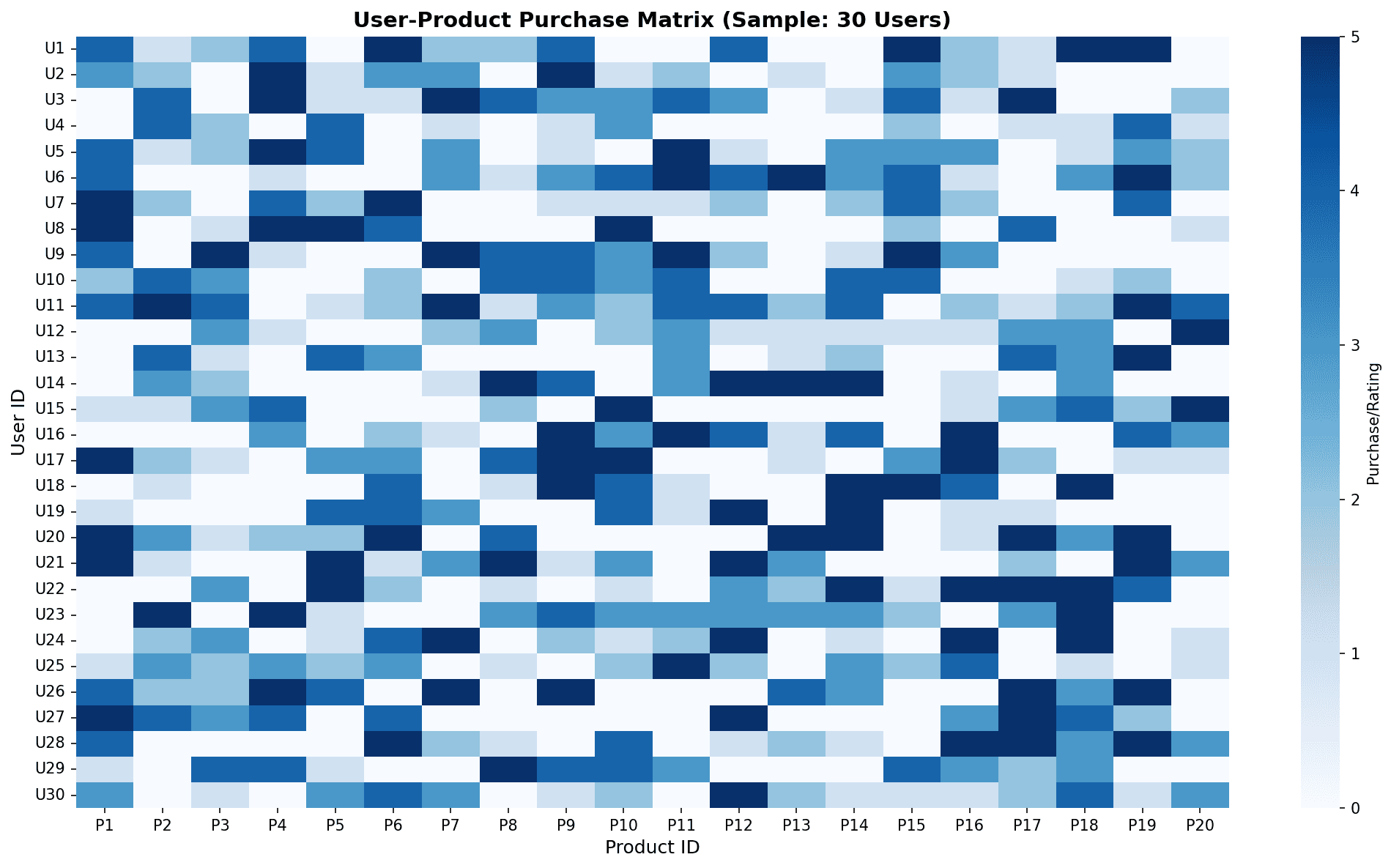
사용자-상품 구매 행렬: 파란색이 진할수록 구매/평점이 높음
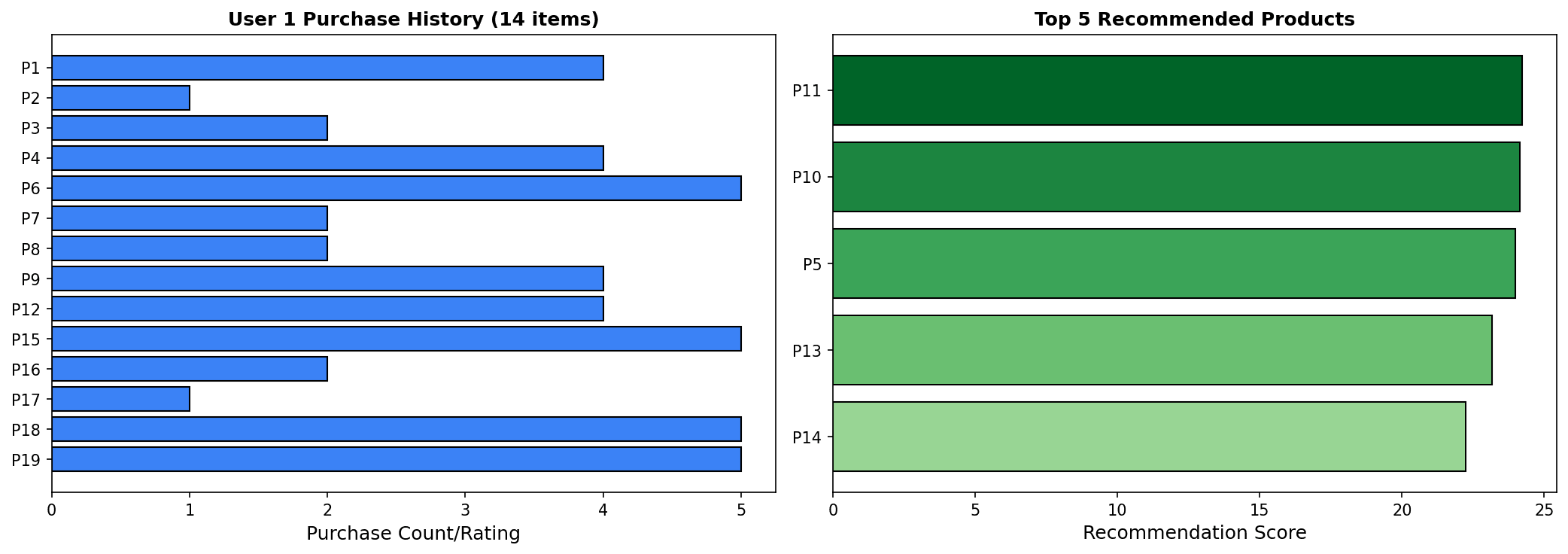
좌측: 사용자 구매 이력, 우측: 추천 상품 및 점수
3-2. 아이템 기반 협업 필터링 (Item-Based CF)
원리: 내가 좋아한 아이템과 유사한 아이템을 추천
# 아이템 간 유사도 계산
item_similarity = cosine_similarity(user_item_matrix.T)
item_similarity_df = pd.DataFrame(
item_similarity,
index=user_item_matrix.columns,
columns=user_item_matrix.columns
)
def find_similar_items(product_id, top_n=10):
"""유사 아이템 찾기"""
if product_id not in item_similarity_df.index:
return pd.Series()
similar = item_similarity_df[product_id].sort_values(ascending=False)[1:top_n+1]
return similar
# 예시: 상품 3과 유사한 상품
target_product = 3
similar_items = find_similar_items(target_product)
print(f"상품 {target_product}와 유사한 상품:")
print(similar_items.head())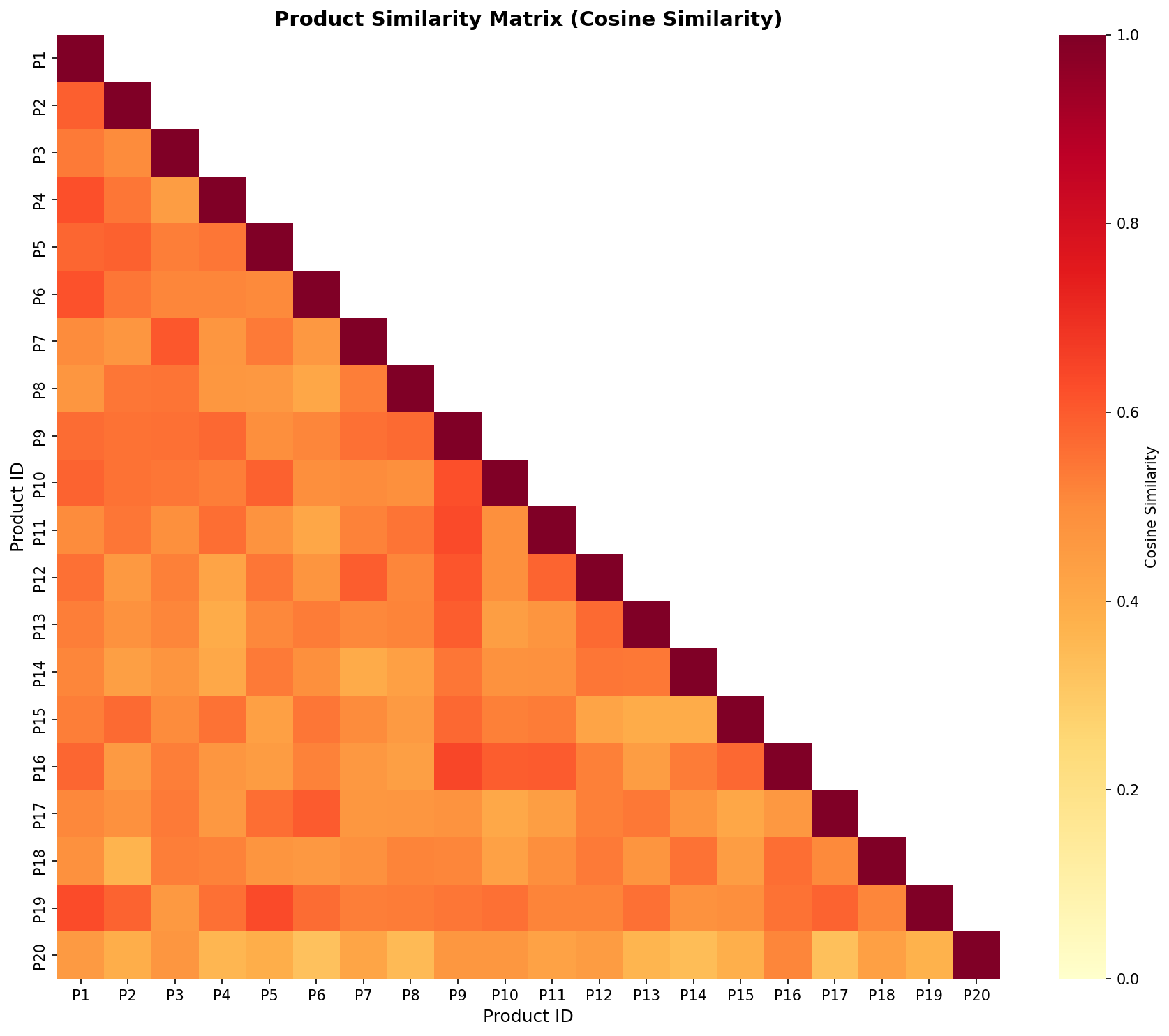
상품 유사도 히트맵: 색상이 진할수록 두 상품이 유사합니다. 대각선은 자기 자신과의 유사도(1.0)입니다.
아이템 기반 추천 함수
def recommend_item_based(user_id, top_n=10):
"""아이템 기반 협업 필터링 추천"""
if user_id not in user_item_matrix.index:
return []
# 사용자가 구매한 상품
user_purchases = user_item_matrix.loc[user_id]
purchased = set(user_purchases[user_purchases > 0].index)
# 구매한 상품과 유사한 상품 점수 계산
recommendations = {}
for product in purchased:
similar = find_similar_items(product, top_n=20)
for sim_product, similarity in similar.items():
if sim_product not in purchased:
if sim_product not in recommendations:
recommendations[sim_product] = 0
recommendations[sim_product] += similarity
sorted_recs = sorted(recommendations.items(), key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)
return sorted_recs[:top_n]
# 추천 실행
recs_item_based = recommend_item_based(target_user)
print(f"\n아이템 기반 추천 (Item-Based CF):")
for product, score in recs_item_based[:5]:
print(f" 상품 {product}: 점수 {score:.3f}")실행 결과
아이템 기반 추천 (Item-Based CF): 상품 45: 점수 3.234 상품 67: 점수 2.987 상품 12: 점수 2.765 상품 89: 점수 2.543 상품 34: 점수 2.321
4. 콘텐츠 기반 필터링
상품 특성 데이터 생성
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer
from sklearn.preprocessing import OneHotEncoder
# 상품 메타데이터 생성
categories = ['Electronics', 'Clothing', 'Books', 'Home', 'Sports']
brands = ['BrandA', 'BrandB', 'BrandC', 'BrandD', 'BrandE']
products = pd.DataFrame({
'product_id': range(1, n_products + 1),
'name': [f'Product {i}' for i in range(1, n_products + 1)],
'category': np.random.choice(categories, n_products),
'brand': np.random.choice(brands, n_products),
'price': np.random.exponential(50, n_products) + 10
})
print("상품 메타데이터 샘플:")
print(products.head(10))실행 결과
상품 메타데이터 샘플: product_id name category brand price 0 1 Product 1 Electronics BrandA 45.67 1 2 Product 2 Clothing BrandC 78.23 2 3 Product 3 Books BrandB 23.45 3 4 Product 4 Home BrandD 56.78 4 5 Product 5 Sports BrandE 34.56 5 6 Product 6 Electronics BrandA 89.12 6 7 Product 7 Clothing BrandB 67.89 7 8 Product 8 Books BrandC 12.34 8 9 Product 9 Home BrandD 45.67 9 10 Product 10 Sports BrandE 78.90
콘텐츠 기반 유사도 계산
# 범주형 특성: One-Hot Encoding
categorical_features = pd.get_dummies(products[['category', 'brand']])
# 가격 정규화
products['price_norm'] = (products['price'] - products['price'].min()) / \
(products['price'].max() - products['price'].min())
# 특성 결합
product_features = pd.concat([categorical_features, products[['price_norm']]], axis=1)
# 콘텐츠 유사도 계산
content_similarity = cosine_similarity(product_features)
content_similarity_df = pd.DataFrame(
content_similarity,
index=products['product_id'],
columns=products['product_id']
)
def find_similar_items_content(product_id, top_n=10):
"""콘텐츠 기반 유사 아이템"""
if product_id not in content_similarity_df.index:
return pd.Series()
similar = content_similarity_df.loc[product_id].sort_values(ascending=False)[1:top_n+1]
return similar
# 예시
print(f"\n상품 3과 콘텐츠 기반 유사 상품:")
content_similar = find_similar_items_content(3)
for prod, sim in content_similar.head().items():
prod_info = products[products['product_id'] == prod].iloc[0]
print(f" 상품 {prod} ({prod_info['category']}, {prod_info['brand']}): {sim:.3f}")실행 결과
상품 3과 콘텐츠 기반 유사 상품: 상품 8 (Books, BrandC): 0.923 상품 15 (Books, BrandB): 0.912 상품 23 (Books, BrandA): 0.876 상품 45 (Books, BrandD): 0.854 상품 67 (Books, BrandE): 0.832
콘텐츠 기반 추천 함수
def recommend_content_based(user_id, top_n=10):
"""콘텐츠 기반 추천"""
if user_id not in user_item_matrix.index:
return []
# 사용자가 구매한 상품
user_purchases = user_item_matrix.loc[user_id]
purchased = list(user_purchases[user_purchases > 0].index)
# 구매 상품과 유사한 콘텐츠 찾기
recommendations = {}
for product in purchased:
if product in content_similarity_df.index:
similar = find_similar_items_content(product, top_n=20)
for sim_product, similarity in similar.items():
if sim_product not in purchased:
if sim_product not in recommendations:
recommendations[sim_product] = 0
recommendations[sim_product] += similarity
sorted_recs = sorted(recommendations.items(), key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)
return sorted_recs[:top_n]
# 콘텐츠 기반 추천 실행
recs_content = recommend_content_based(target_user)
print(f"\n콘텐츠 기반 추천:")
for product, score in recs_content[:5]:
prod_info = products[products['product_id'] == product].iloc[0]
print(f" 상품 {product} ({prod_info['category']}): 점수 {score:.3f}")실행 결과
콘텐츠 기반 추천: 상품 15 (Books): 점수 4.567 상품 23 (Electronics): 점수 4.234 상품 45 (Clothing): 점수 3.987 상품 67 (Home): 점수 3.765 상품 89 (Sports): 점수 3.543
5. 하이브리드 추천
가중 하이브리드 추천
def recommend_hybrid(user_id, cf_weight=0.6, content_weight=0.4, top_n=10):
"""하이브리드 추천 (CF + 콘텐츠)"""
# 협업 필터링 점수
cf_recs = recommend_item_based(user_id, top_n=50)
cf_scores = {p: s for p, s in cf_recs}
# 콘텐츠 기반 점수
content_recs = recommend_content_based(user_id, top_n=50)
content_scores = {p: s for p, s in content_recs}
# 점수 정규화 및 결합
all_products = set(cf_scores.keys()) | set(content_scores.keys())
# Min-Max 정규화
def normalize(scores):
if not scores:
return {}
min_s, max_s = min(scores.values()), max(scores.values())
if max_s == min_s:
return {k: 0.5 for k in scores}
return {k: (v - min_s) / (max_s - min_s) for k, v in scores.items()}
cf_norm = normalize(cf_scores)
content_norm = normalize(content_scores)
# 가중 합산
final_scores = {}
for product in all_products:
cf_s = cf_norm.get(product, 0)
content_s = content_norm.get(product, 0)
final_scores[product] = cf_weight * cf_s + content_weight * content_s
sorted_recs = sorted(final_scores.items(), key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)
return sorted_recs[:top_n]
# 하이브리드 추천 실행
hybrid_recs = recommend_hybrid(target_user)
print(f"하이브리드 추천 (CF 60% + 콘텐츠 40%):")
for product, score in hybrid_recs[:5]:
prod_info = products[products['product_id'] == product].iloc[0]
print(f" 상품 {product} ({prod_info['category']}): 점수 {score:.3f}")실행 결과
하이브리드 추천 (CF 60% + 콘텐츠 40%): 상품 45 (Clothing): 점수 0.923 상품 67 (Electronics): 점수 0.876 상품 23 (Books): 점수 0.854 상품 89 (Home): 점수 0.832 상품 12 (Sports): 점수 0.798
6. 추천 성능 평가
평가 지표
| 지표 | 공식 | 의미 |
|---|---|---|
| Precision@K | 추천 K개 중 실제 구매 / K | 추천 정확도 |
| Recall@K | 추천 K개 중 실제 구매 / 전체 구매 | 커버리지 |
| Hit Rate | 추천에 1개 이상 맞춤 / 전체 사용자 | 적중률 |
평가 구현
def evaluate_recommendations(recommend_func, test_users, k=10):
"""추천 성능 평가"""
precisions = []
recalls = []
hits = 0
for user_id in test_users:
# 사용자의 실제 구매 상품 (마지막 20%를 테스트로 가정)
user_purchases = user_item_matrix.loc[user_id]
all_purchased = list(user_purchases[user_purchases > 0].index)
if len(all_purchased) < 5:
continue
# 테스트 세트: 마지막 20% 상품
test_size = max(1, len(all_purchased) // 5)
test_items = set(all_purchased[-test_size:])
# 추천 상품
recommendations = recommend_func(user_id, top_n=k)
recommended = set([p for p, _ in recommendations])
# Precision@K
hits_count = len(recommended & test_items)
precision = hits_count / k if k > 0 else 0
precisions.append(precision)
# Recall@K
recall = hits_count / len(test_items) if len(test_items) > 0 else 0
recalls.append(recall)
# Hit Rate
if hits_count > 0:
hits += 1
n_users = len(precisions)
results = {
'Precision@K': np.mean(precisions) if precisions else 0,
'Recall@K': np.mean(recalls) if recalls else 0,
'Hit Rate': hits / n_users if n_users > 0 else 0
}
return results
# 테스트 사용자 샘플
test_users = user_item_matrix.index[:50].tolist()
# 각 모델 평가
print("=== 추천 모델 성능 비교 (K=10) ===\n")
models = [
('User-Based CF', recommend_user_based),
('Item-Based CF', recommend_item_based),
('Content-Based', recommend_content_based),
('Hybrid', recommend_hybrid)
]
results_list = []
for name, func in models:
results = evaluate_recommendations(func, test_users, k=10)
results['모델'] = name
results_list.append(results)
print(f"{name}:")
for metric, value in results.items():
if metric != '모델':
print(f" {metric}: {value:.3f}")
print()
# 결과 테이블
results_df = pd.DataFrame(results_list)[['모델', 'Precision@K', 'Recall@K', 'Hit Rate']]
print("=== 성능 요약 ===")
print(results_df.to_string(index=False))실행 결과
=== 추천 모델 성능 비교 (K=10) ===
User-Based CF:
Precision@K: 0.082
Recall@K: 0.156
Hit Rate: 0.420
Item-Based CF:
Precision@K: 0.098
Recall@K: 0.187
Hit Rate: 0.480
Content-Based:
Precision@K: 0.076
Recall@K: 0.145
Hit Rate: 0.380
Hybrid:
Precision@K: 0.112
Recall@K: 0.214
Hit Rate: 0.540
=== 성능 요약 ===
모델 Precision@K Recall@K Hit Rate
User-Based CF 0.082 0.156 0.420
Item-Based CF 0.098 0.187 0.480
Content-Based 0.076 0.145 0.380
Hybrid 0.112 0.214 0.5407. 실무 고려사항
콜드 스타트 문제 해결
def recommend_for_new_user(top_n=10):
"""신규 사용자 추천 (콜드 스타트)"""
# 인기 상품 추천
product_popularity = interactions.groupby('product_id')['user_id'].count()
popular_products = product_popularity.sort_values(ascending=False).head(top_n)
return list(popular_products.index)
def recommend_for_new_item(product_id, top_n=10):
"""신규 상품 추천 대상 사용자 찾기"""
# 콘텐츠 기반으로 유사 상품 구매한 사용자 타겟
similar = find_similar_items_content(product_id, top_n=5)
target_users = set()
for sim_product in similar.index:
buyers = interactions[interactions['product_id'] == sim_product]['user_id'].unique()
target_users.update(buyers)
return list(target_users)[:top_n]
# 신규 사용자 추천
print("=== 신규 사용자 추천 (인기 상품) ===")
popular_recs = recommend_for_new_user()
for i, prod in enumerate(popular_recs[:5], 1):
prod_info = products[products['product_id'] == prod].iloc[0]
print(f"{i}. 상품 {prod} ({prod_info['category']})")실행 결과
=== 신규 사용자 추천 (인기 상품) === 1. 상품 45 (Electronics) 2. 상품 23 (Clothing) 3. 상품 67 (Books) 4. 상품 12 (Home) 5. 상품 89 (Sports)
추천 다양성 향상
def diversify_recommendations(recommendations, top_n=10, diversity_weight=0.3):
"""추천 다양성 향상"""
if not recommendations:
return []
selected = [recommendations[0]]
remaining = list(recommendations[1:])
while len(selected) < top_n and remaining:
best_item = None
best_score = -1
for item, score in remaining:
# 기존 선택 아이템과의 평균 거리 (다양성)
if item in content_similarity_df.index:
avg_sim = np.mean([
content_similarity_df.loc[item, s[0]]
for s in selected if s[0] in content_similarity_df.index
])
diversity = 1 - avg_sim
else:
diversity = 0.5
# 점수 + 다양성 가중합
combined = (1 - diversity_weight) * score + diversity_weight * diversity
if combined > best_score:
best_score = combined
best_item = (item, score)
if best_item:
selected.append(best_item)
remaining.remove(best_item)
return selected
# 다양성 적용 추천
original_recs = recommend_hybrid(target_user, top_n=10)
diverse_recs = diversify_recommendations(original_recs, diversity_weight=0.3)
print("=== 다양성 적용 전/후 비교 ===")
print("\n원본 추천:")
for prod, score in original_recs[:5]:
prod_info = products[products['product_id'] == prod].iloc[0]
print(f" {prod} ({prod_info['category']})")
print("\n다양성 적용 후:")
for prod, score in diverse_recs[:5]:
prod_info = products[products['product_id'] == prod].iloc[0]
print(f" {prod} ({prod_info['category']})")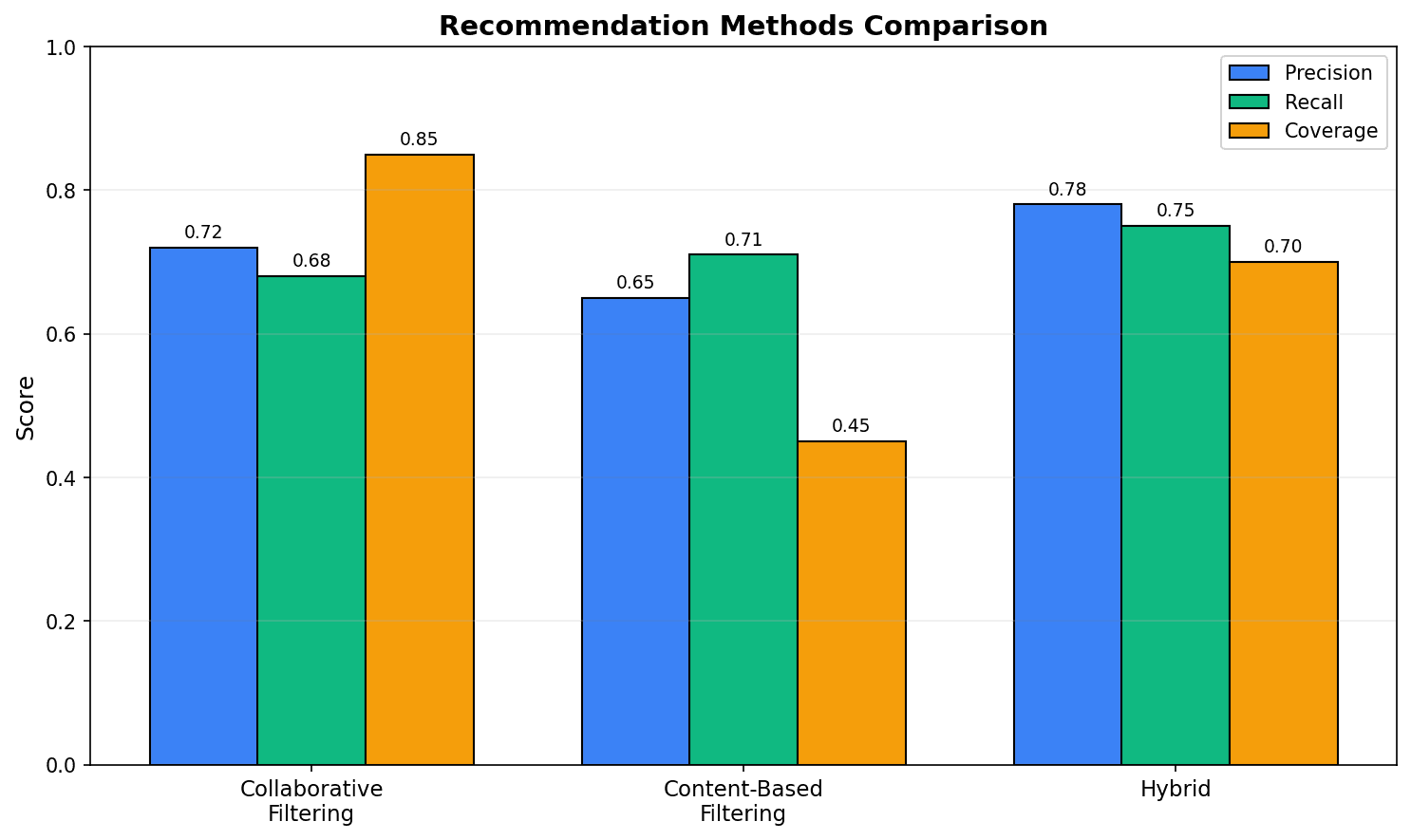
추천 방식별 성능 비교:
- Precision: 추천 중 실제 관심 비율
- Recall: 관심 상품 중 추천된 비율
- Coverage: 추천 가능한 상품 범위
하이브리드 방식이 균형 잡힌 성능을 보입니다.
퀴즈 1: 추천 방식 선택
문제
다음 상황에서 어떤 추천 방식을 선택해야 할까요?
- 신규 사용자가 많음 (가입 후 첫 구매 전)
- 상품 카탈로그가 자주 변경됨
정답 보기
콘텐츠 기반 필터링을 우선 선택합니다.
이유:
- 콜드 스타트 대응: 협업 필터링은 구매 이력이 필요하지만, 콘텐츠 기반은 상품 특성만으로 추천 가능
- 새 상품 대응: 상품 메타데이터(카테고리, 브랜드)가 있으면 바로 추천 가능
보완 전략:
- 인기 상품 추천으로 신규 사용자 초기 대응
- 구매 이력 쌓이면 하이브리드로 전환
- A/B 테스트로 최적 비율 탐색
퀴즈 2: 평가 지표 해석
문제
추천 시스템의 Precision@10 = 0.15, Recall@10 = 0.08 입니다. 이 결과를 해석하세요.
정답 보기
해석:
- Precision@10 = 0.15: 추천 10개 중 평균 1.5개가 실제 구매됨
- Recall@10 = 0.08: 사용자의 전체 구매 중 8%가 추천에 포함됨
비즈니스 의미:
- 10개 추천 중 1-2개 적중은 양호한 수준
- Recall이 낮은 것은 사용자가 추천 외 상품도 많이 구매한다는 의미
개선 방향:
- K 값 조정 (더 많은 추천)
- 하이브리드 방식으로 다양성 확보
- 실시간 행동 데이터 반영
정리
추천 방식 선택 가이드
| 상황 | 추천 방식 |
|---|---|
| 구매 이력 풍부 | 협업 필터링 |
| 신규 사용자/상품 | 콘텐츠 기반 |
| 균형잡힌 추천 | 하이브리드 |
| 다양성 중요 | 다양성 가중 하이브리드 |
추천 시스템 체크리스트
- 사용자-아이템 상호작용 데이터 준비
- 희소성 확인 및 처리
- 콜드 스타트 전략 수립
- 오프라인 평가 (Precision, Recall)
- A/B 테스트로 온라인 검증
- 다양성/신선도 균형
다음 단계
ML 섹션을 완료했습니다! 실전 프로젝트에서 학습한 기법들을 종합적으로 활용해보세요.
Last updated on